Introduction
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development technique in which developers use a version control system, like Git, and push code changes daily, multiple times a day. Instead of building out features in isolation and integrating them at the end of the development cycle, a more iterative approach is employed.
- Each merge triggers an automated set of scripts to automatically build and test your application.
- These scripts help decrease the chances that you introduce errors in your application.
- If some of the scripts fail, the CI system doesn't progress to further stages, issuing a report that developers can use to promptly assess what was wrong and resolve the problem.
This reading will teach you why embracing a CI tool is essential for your software development process. You will also explore a typical development workflow that you can integrate into your CI system and some of the main benefits of using CI.
Why do we need CI?
In new product development, the time to figure everything out up front is limited. Taking smaller steps helps estimate more accurately and validate more often. Having a shorter feedback loop involves more iterations. This number of iterations, not the number of hours invested, drives the process forward.
Working in long feedback loops is risky for software development teams, increasing the chances of introducing errors. Integrating new changes is also time-consuming.
By automating all integration steps and having small controlled changes, developers avoid repetitive work and minimize human errors. The CI tool monitors the central code repository and prevents people from deciding when and how to run tests. Every time there is a new commit, it runs all automated tests.
Based on the outcome, it either accepts the commit if all tests passed successfully or reject it if there was a failure.
CI Pipeline
Below is a graphical representation of a typical CI process as a pipeline. When new code enters one end, a new version of the app gets built automatically, and a suite of automated tests is run against it.
Continuous Integration is a small part of a more significant process called Continuous Delivery. However, that's outside the scope of the purpose of this lesson, and you can check more information in the additional resources section.
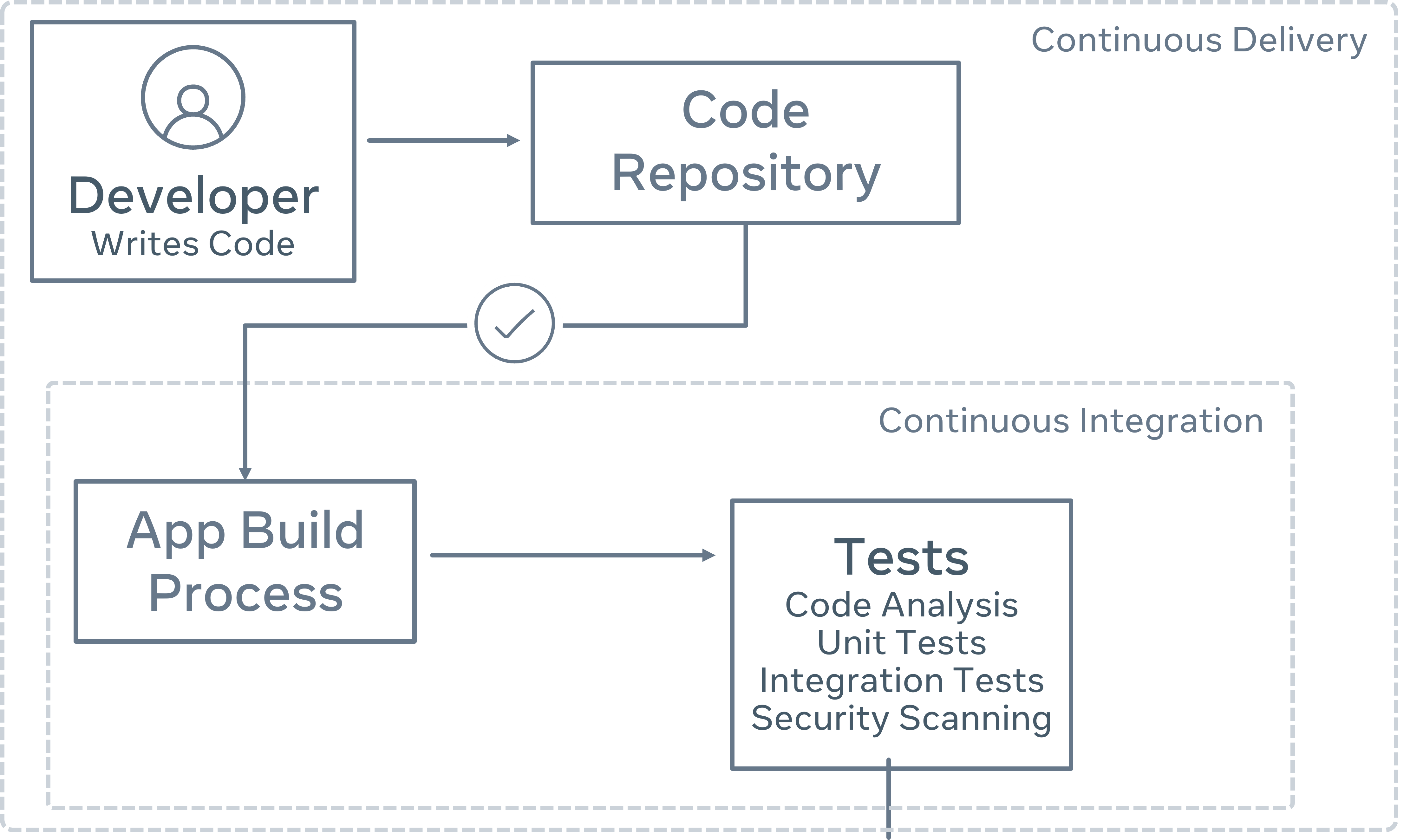
A typical development workflow
Here is a simplified CI workflow that companies often embrace daily as part of their software development process:
- A developer from the team creates a new branch of code in Github, performs changes in the code, and commits them.
- When the developer pushes its work to GitHub, the CI system builds the code on its servers and runs the automated test suite.
- Suppose the CI system detects any error in the CI pipeline. In that case, the developer who pushed the code gets a notification, for example, via email, and the status of CI changes to red. The developer is responsible for analyzing what went wrong and fixing the problem.
- Otherwise, if the status is green and all goes well, the pipeline moves to its next stage, which usually involves deploying a new version of the application to a staging server. This new version can be used internally by the Quality Assurance (QA) team to verify the changes in a production-like environment.
Benefits of continuous integration
Some of the benefits for your software development teams are:
- Improved developer productivity: CI frees developers from manual tasks and the pain of integrating their code with other system parts. They can instead focus on programming the logic that delivers the business's desired features.
- Deliver working software more often: CI is a way for your team to build and test every source code change automatically. This fast CI feedback loop delivers more value to customers than teams that rely on manual integrations of each other's work. This foundation enables a software delivery process to be efficient, resilient, fast, and secure.
- Find bugs earlier, and fix them faster: The automated testing process can include different checks, like verifying code correctness, validating application behavior, or making sure the coding style follows industry-standard conventions. A CI tool provides instant feedback to developers on whether the new code they wrote works or introduces bugs or regression in quality. Mistakes that are caught early on are the easiest to fix.
Conclusion
In this reading, you have had an introduction to continuous Integration and why embracing a CI tool is important for your software development process.
You also learned about a typical development workflow that can be integrated into your CI system and explored some of the main benefits of using CI.