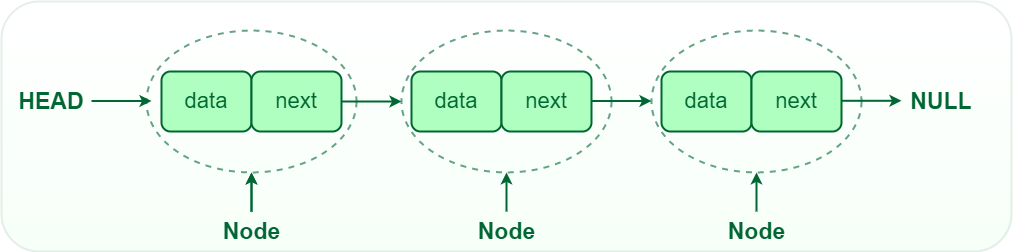
Linked List
- A linked list is a linear data structure that stores data in nodes, which are connected by pointers. Pointer is the address of the next node that is linked with previous node.
- Unlike arrays, linked lists are not stored in contiguous memory locations.
- It take dynamic memory allocation efficient in insertion and deletion operations compared to the arrays.
Characteristics of Linked List:
- Dynamic: Linked lists can be easily resized by adding or removing nodes.
- Non-contiguous: Nodes are stored in random memory locations and connected by pointers.
- Sequential access: Nodes can only be accessed sequentially, starting from the head of the list.
- Insert in O(1).
- Searching: Time complexity is O(n) big of n.
tip
If you are insert the data within the existing list then you can used the Linked List b/c its time complexity is less then array, and if you are searching the data then you can used the array b/c time complexity of array is O(1) and linked list is O(n).
Operations on Linked List:
- Creation: Creating a new linked list or adding a new node to an existing list.
- Traversal: Iterating through the list and accessing each node.
- Insertion: Adding a new node at a specific position in the list.
- Deletion: Removing a node from the list.
- Search: Finding a node with a specific value in the list.
Types of Linked List:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Circular Doubly Linked List
- Header Linked List